In the realm of construction, foundations is certainly one of the most critical elements of every structure. Among the different kinds of foundations, pile foundations are notable for their ability to provide solid support in difficult ground conditions. Whether you're constructing a skyscraper in a city setting or a bridge over water, comprehending piling foundations is important for ensuring the longevity and safety of a project. In this piece, we will examine the vital role of piling foundations, outlining their function, installation processes, and the various types available.
For novices in construction and engineering, the concept of piling foundations can seem complex. However, this guide will break down the essentials, explaining how piling foundations work and why they are necessary for stability in different construction contexts. We will address everything from the differences between shallow and deep foundations to the materials frequently employed in pile construction, helping you grasp the significance of this crucial aspect of modern engineering.
Grasping Drilled Base Structures
Drilled foundations are specialized types of foundations utilized to underpin edifices by shifting forces to lower, more stable soil or bedrock strata. They consist of long, narrow columns injected far into the ground, which helps in achieving firmness when building on weak or insecure ground. Their chief role is to deliver enhanced support for large buildings, such as towering buildings, spans, and wharves, where standard less deep foundations would be insufficient.
The implementation of piled bases entails different approaches, including hammered columns, which are hammered into the earth, and bored columns, which are constructed by drilling into the earth and then pouring it with cement. The selection of technique often is determined by the location conditions, the kind of structure being constructed, and the environmental considerations. By applying the correct type of piling foundation, engineers can reduce risks associated with ground movements and ensure perpetual constructional integrity.
Understanding the various types of piled bases is crucial for successful construction planning. Typical kinds include iron columns, cement columns, and timber columns, each with its distinct advantages and limitations. In particular, innovations in piled technology have improved the efficiency and capability of these bases, enabling better performance in difficult conditions. These innovations have made piling a preferred option in current construction endeavors, especially in city or shoreline environments where soil conditions may change greatly.
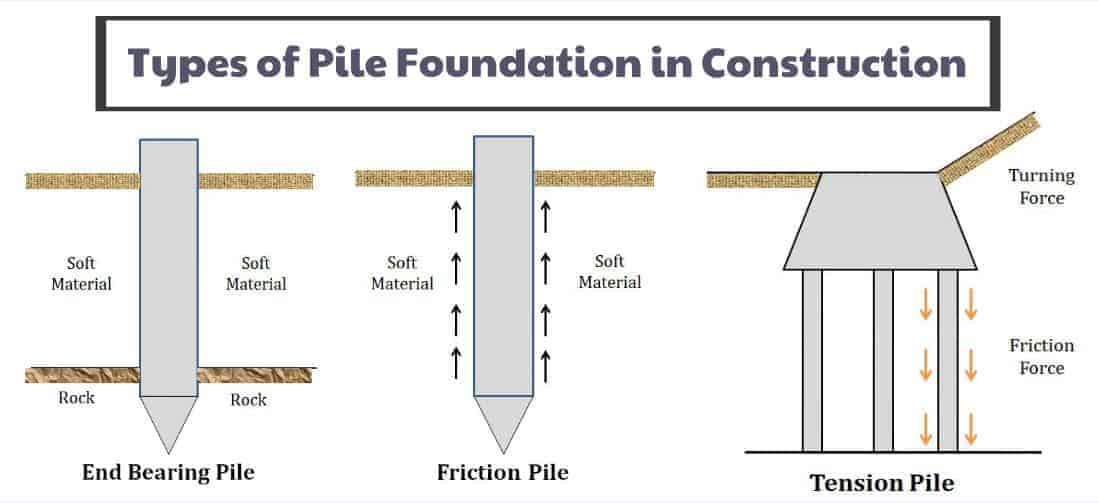
Types and Uses of Pile Foundations
Piling foundations come in multiple forms, which are designed to address specific soil conditions and structural requirements. The two primary categories are driven piles and drilled piles. Driven dublin city roofers are prefabricated columns that are hammered into the ground using a pile driver. They are typically made from materials like concrete, steel, or timber and are well-suited for uses where there is strong soil to bore through. In contrast, drilled piles are formed by drilling a hole into the ground and then packing it with concrete or other materials. This method is often used in locations with limited access or in areas with sensitive environmental considerations.
Uses of pile foundations are vast and diverse. In urban construction, they are essential for supporting skyscrapers, bridges, and other large structures that require a secure base. Piling is also crucial in coastal construction, where the soil conditions can be difficult due to erosion and fluctuating water levels. Moreover, these foundations are increasingly used in projects where traditional foundations would not be adequate, such as on redeveloped land or in areas with unstable soil conditions.
The choice of the appropriate type of piling foundation depends on multiple factors, including soil characteristics, structural loads, and environmental conditions. Engineers evaluate the site to determine which type of pile will provide the necessary support and stability for the building. Innovations in piling technology continue to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of these foundations, making them a favored choice in modern construction.
### Installation and Cost Considerations
Installing piling foundations requires meticulous planning and execution, as multiple factors influence the process. The site conditions, such as soil characteristics, water table level, and the presence of subsurface utilities, are crucial in determining the installation method. Typically, impact piles are installed using percussive hammers or vibration hammers, while drilled piles are created by boring a hole and then inserting concrete or steel into it. The choice between these methods can also affect the project timeline and complexity, where driven columns may offer more rapid installation but might create disturbance and vibrations that can impact surrounding areas.
Cost considerations for piling foundations can vary significantly based on various elements. The materials chosen, whether metal or concrete, directly impact overall expenses, with pricing fluctuating based on market conditions. Additionally, installation methods, mobilization of equipment, and labor costs play a vital role in the total project budget. It's important to conduct a thorough analysis and consider all cost factors to ensure the project remains financially viable while meeting structural needs.
Despite potentially higher initial costs, investing in piling foundations often pays off in sustained stability and safety, especially in challenging soil conditions. Carefully designed and installed piles can prevent issues such as foundation settlement, ultimately extending the building's lifespan. When evaluating costs, it's crucial to weigh the upfront investment against the future benefits of improved structural integrity and lower maintenance expenses, ensuring that piling foundations align with the project's goals.
