Piling footings play a vital role in the building sector, offering a strong base for buildings built on less than ideal soil situations. As CFA Piling Derby grow taller and larger, the issues related to supporting such loads become increasingly complex. This is where drilled foundations come into play, enabling engineers to extend structural reinforcement deep into the earth where stronger soil or bedrock is found. Grasping how these footings work and their importance in contemporary construction is essential for those involved in construction endeavors.
In this piece, we will explore the different types of piling foundations, the innovations influencing their use, and the key factors that impact their design and erection. From the advantages they offer in terms of structural integrity to the obstacles faced during construction, we aim to provide a thorough overview for both beginners and experienced experts alike. Whether you are considering a new building project or simply want to gain knowledge more about this vital aspect of civil engineering, this exploration into piling foundations will equip you with the insight needed to navigate this complex field.
Comprehending Foundation Base Structures
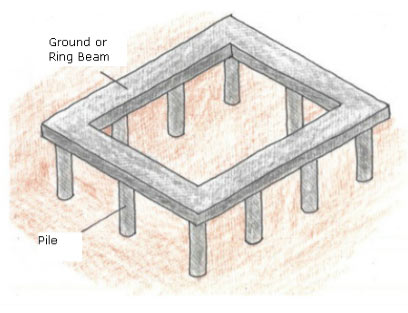
Piling foundations are a vital component in current building, particularly for structures that require support large loads or are constructed on challenging ground conditions. They consist of elongated, slender columns or columns, termed as stakes, that are installed deep into the ground to reach a stronger ground stratum or foundation rock. This method improves the strength and support of buildings, overpasses, and other facilities, ensuring safety and durability.
The importance of piling bases lies in their capability to distribute load from the upper structure to the subsurface, further reliable layers of soil. Traditional bases might not be enough in locations with low weight-supporting capacity or when building elevated tower structures. Piles can be made of different materials, including cement, steel, and wood, allowing for flexibility in design and implementation based on the specific requirements of each project.
When preparing for a building initiative, engineers evaluate ground conditions, building requirements, and environmental aspects to determine if piling bases are necessary. This approach not only accommodates big structures but also addresses concerns such as ground subsidence, environmental impact, and overall stability. With innovations in techniques, the processes surrounding the design and installation of piling bases continue to advance, providing safety and efficiency in construction practices.
Breakthroughs and Methods in Piling
New developments in piling technology have transformed how foundations are created and built. The adoption of advanced resources, such as superior concrete and composite materials, has enhanced the durability and durability of piles. These innovations allow for more streamlined and optimized designs that reduce overall project costs while improving structural performance. Moreover, the use of modular construction techniques for piling elements accelerates the installation process, minimizes waste, and cuts project timelines.
Instrumentation developments in instrumentation and monitoring have also played a key role in contemporary piling foundations. Engineers now use sophisticated load testing equipment and sensors to assess the capabilities of piles during and after installation. These instruments provide real-time data that helps engineers make educated decisions, ensuring that the foundation meets necessary safety and load standards. Furthermore, advancements in computer simulation and forecasting allow for better forecasting of load responses, making it possible to design more effective foundation systems tailored to particular site conditions.
Additionally, innovations in piling installation machinery have boosted the efficiency of foundation work. For example, the development of rotary drilling rigs and vibratory pile drivers has made it easier to install deep foundations in challenging soil conditions. These machines facilitate quicker and more precise pile installations, minimizing disruption to surrounding areas. As the industry continues to progress, integrating automation and robotics into piling operations holds the potential to further revolutionize the construction process, paving the way for more intelligent and more sustainable building practices.
Challenges and Considerations in Piling Installation
Piling installation introduces several challenges that require careful preparation and implementation. One notable issue is the geological differences of the area. Different soil types can influence the choice of pile type, depth, and installation method. Engineers must conduct extensive site investigations to understand soil conditions, which can be labor-intensive. Unexpected soil layers or underground obstacles, like boulders can prolong the project and require changes to the installation plan.
Another factor is the potential influence on surrounding structures and the environment. Vibration and noise during piling installation can disturb adjacent buildings and communities. Engineers and contractors must implement measures to reduce disruption, which may include using quieter installation methods or scheduling work at specific times. Furthermore, environmental regulations may impose extra requirements for noise and vibration control, adding difficulty to the project.
Lastly, safety is critical during piling installation. The use of heavy machinery and the deep excavation required pose risks to workers in the area. Ensuring proper training, adherence to safety protocols, and effective communication among team members is important to prevent accidents. Additionally, maintaining equipment and monitoring the installation process helps ensure the integrity of the piles, contributing to both project safety and long-term structural stability.
